In rare cases it could be a hacker
Does nothing happen when you click or tap the Back button on your web browser? Does it simply reload the current page instead? Or does the Back button appear grayed out?
Usually, the Back button in a browser fails to function correctly due to reasons such as redirecting links and conflicting browser extensions. But rarely, you could be dealing with something as serious as a malicious add-on or browser hijacker.
Work your way through the list of suggestions and solutions below to fix when the Back button is not working in Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, Microsoft Edge, and Apple Safari.
Switch Tabs or Windows
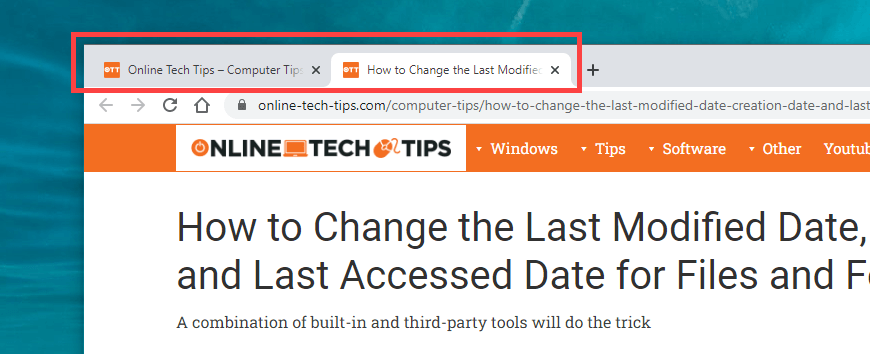
Most links that you click on tend to open in the same browser tab. But if the Back button on a page that you just loaded appears grayed out, that’s likely because it opened up in a new tab or window.
In that case, you can’t use the Back button. The only way to go back to the previous page is to switch tabs or windows.
If you use an extension that forces your browser to open links in new tabs or windows, you may want to disable it (more on that further below).
Multiple Redirects
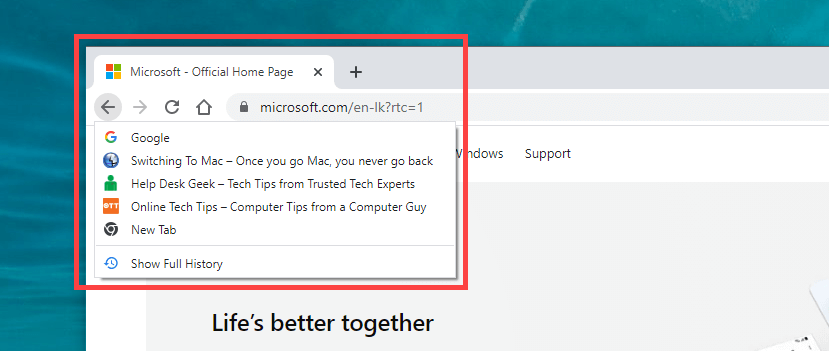
Some links redirect through one or more web addresses before loading. When that happens, selecting the Back button may cause it to reload the same page.
One way to overcome the issue is to long-click the Back button. That prompts browsers such as Chrome to display the history stack for the tab. Then, simply select the page you want to get to, and you should be able to skip the redirecting addresses. This also works on mobile browsers; just long-tap the Back button to bring up the tab’s history.
Another way to deal with the issue is to click the Back button multiple times rapidly. That helps prevent any previous redirects from kicking into action.
Disable Conflicting Browser Addons
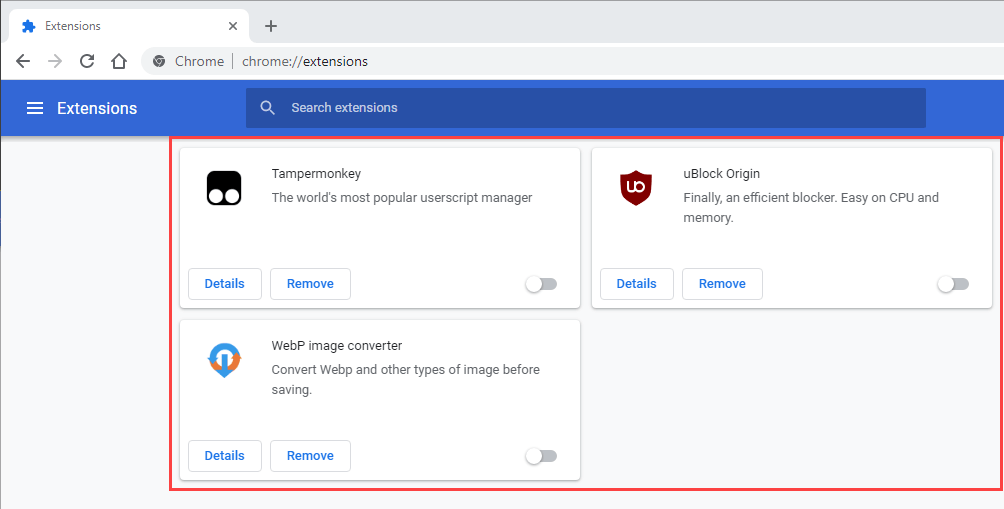
On desktop devices specifically, extensions can prevent the Back button on your browser from working correctly. For example, add-ons such as content blockers and user script managers often cause that. Deactivating them should help.
If you can’t think about anything specific, start by disabling all browser extensions. You can access the Extensions page via your browser’s menu (look for an icon with three dots or lines). In Chrome, for example, select More tools > Extensions on the Chrome menu to bring up your extensions list.
If the Back button begins to work correctly after deactivating all extensions, begin re-enabling them one by one until you figure out what’s causing the problem.
Clear Browser Cache and Cookies
A corrupt or obsolete browser cache is another reason that causes websites or the browser itself to behave incorrectly. If clicking or tapping the Back button doesn’t do anything or causes the same page to reload, clearing it might help fix things. Here’s how to delete the cache in two popular desktop browsers.
Google Chrome
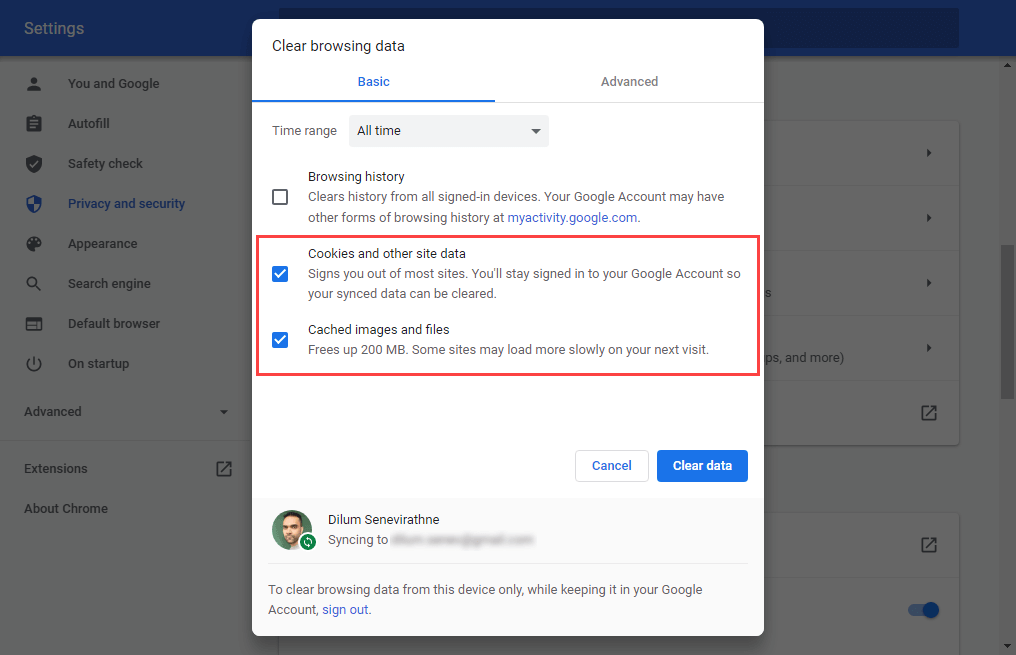
Open the Chrome menu and go to Settings > Privacy and security > Clear browsing data. Next, check the boxes next to Cookies and other site data and Cached images and files, set Time range to All time, and select Clear data.
Mozilla Firefox
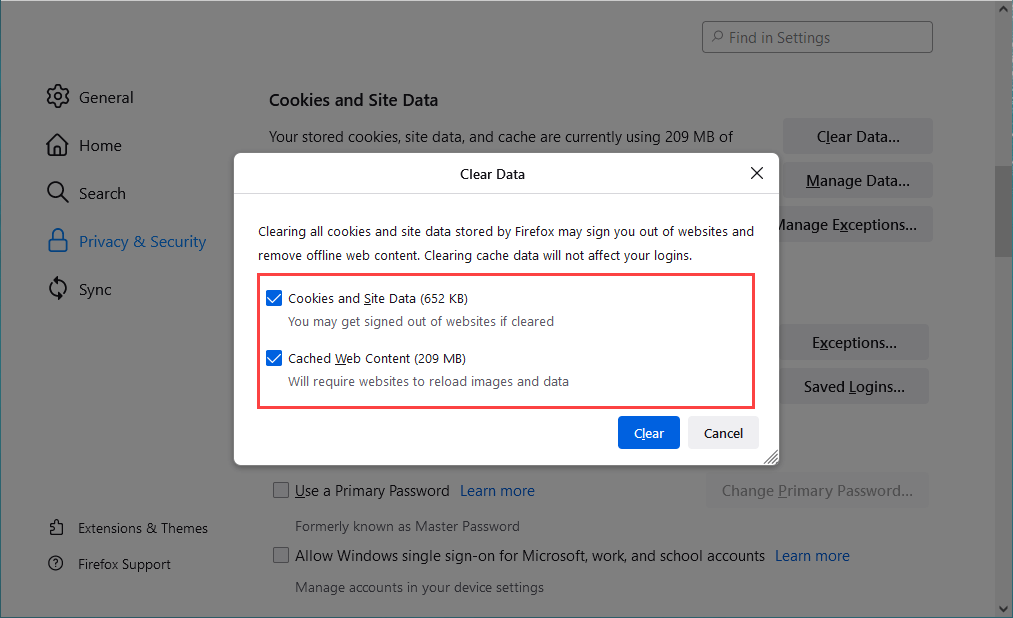
Open the Firefox menu and go to Settings > Privacy & Security > Cookies and Site Data > Clear Data. Next, check the boxes next to Cookies and Site Data and Cached Web Content and select Clear.
If you use a different browser, refer to our master guide to clearing the cache in any browser for specific instructions.
Update Your Web Browser
An outdated browser can result in all sorts of odd issues. If the Back button fails to work for no apparent reason, try installing the latest updates. That should help rule out any known bugs from the equation.
Most desktop browsers auto-update themselves, but you can always initiate a manual check for updates. Here’s how to do that with Chrome and Firefox.
Google Chrome
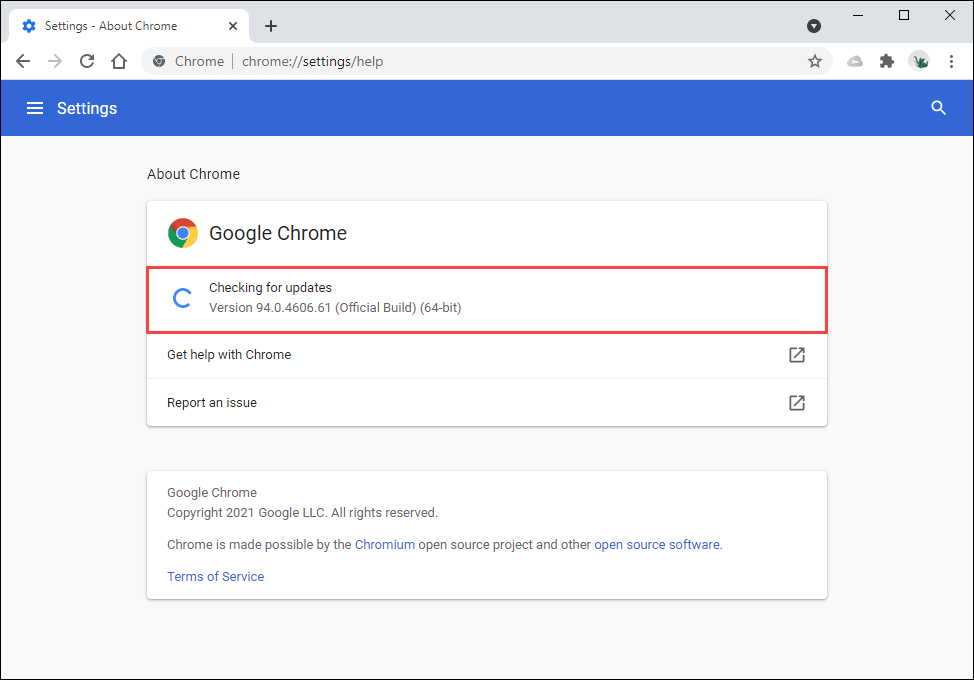
Open the Chrome menu and select Help > About Google Chrome. Then, wait until Chrome searches for the latest updates. If it does detect any updates, it should start installing them automatically.
Mozilla Firefox
Open the Firefox menu and select Help > About Firefox. Then, wait until Firefox searches for and installs the latest updates. Follow that by restarting your browser.
On mobile, you can install the latest browser updates by heading over to the Play Store (Android) or the App Store (iOS).
Check for Malware and Browser Hijackers
Malicious software and add-ons can hijack default browser functionality. Aside from a malfunctioning Back button, you may also notice other unusual behavior, such as slowdowns, crashes, etc.
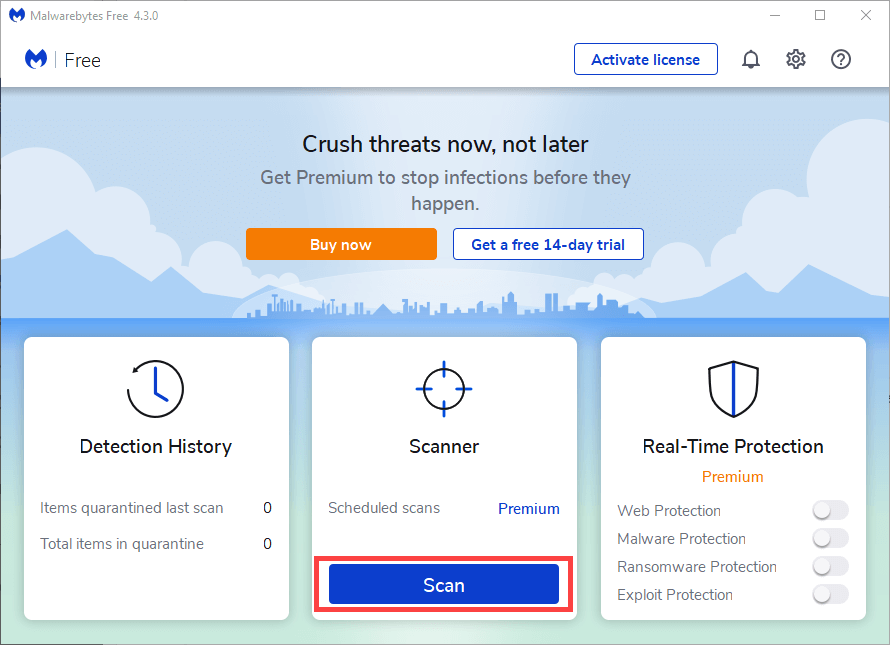
The best way to fix that is by scanning your device using a dedicated malware removal utility. For example, Malwarebytes can help you remove malware on both the PC and Mac.
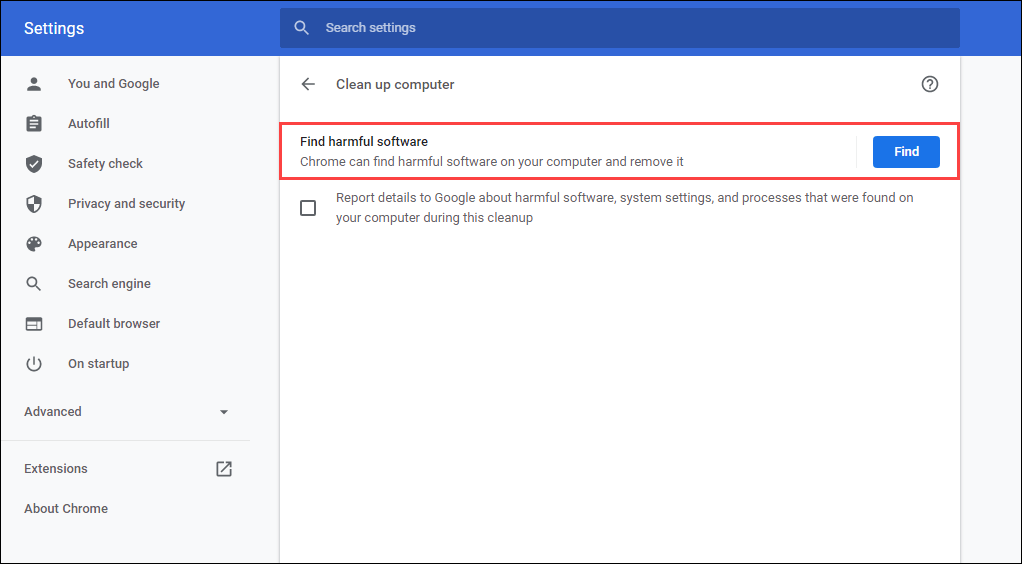
If you use Chrome in Windows, you can also use its built-in malware removal tool to remove malicious extensions and browser hijackers. To run it, open the Chrome menu and select Settings > Advanced > Reset and clean up > Clean up computer > Find.
Reset Your Web Browser
Most desktop web browsers provide a reset option to resolve serious issues. If none of the suggestions or solutions above helped fix the Back button, you should do that now.
Here’s how to reset Chrome and Firefox below. You may want to back up your browsing data by syncing them to a Google Account or Firefox Account before you start. If you use a different browser, look up its support pages online for specific instructions.
Google Chrome
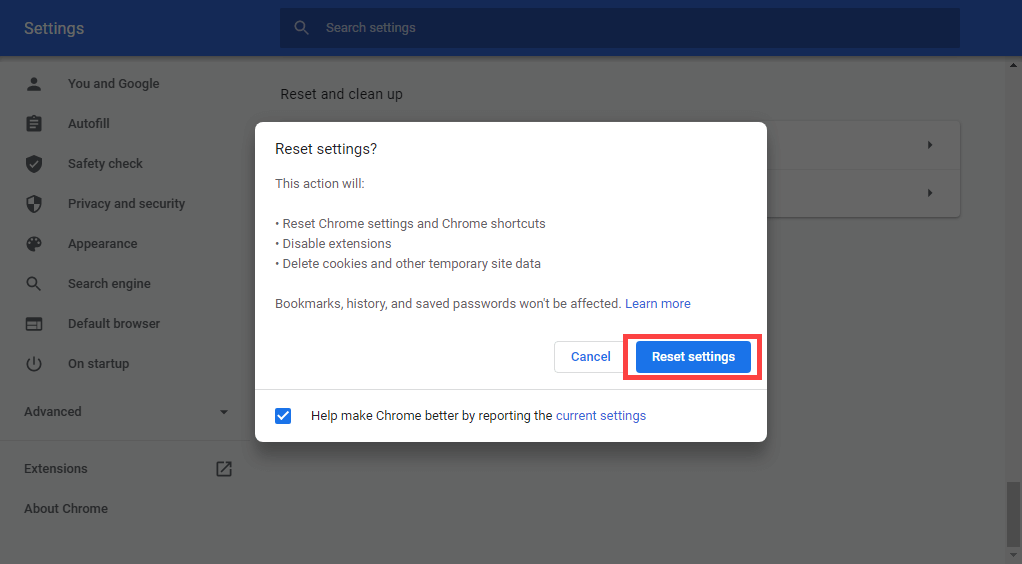
Open the Chrome menu and select Settings. Then, select Advanced > Reset and clean up > Restore settings to their original defaults.
Mozilla Firefox
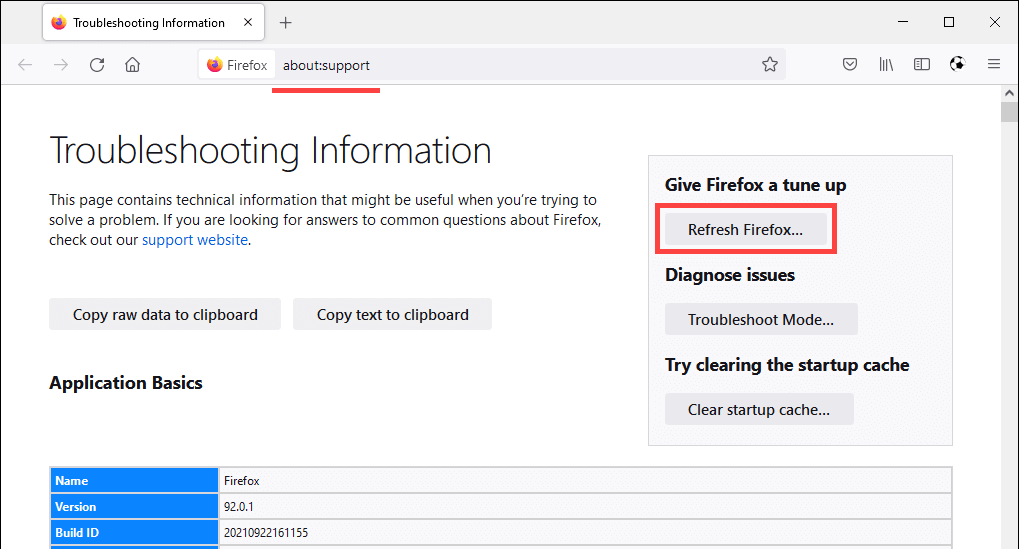
Type about:support into a new Firefox tab and press Enter. Then, select Refresh Firefox.
On mobile, you may want to remove and reinstall your browser to fix any underlying issues preventing the Back button from working. However, that’s not possible with stock mobile browsers such as Chrome (Android) and Safari (iOS).